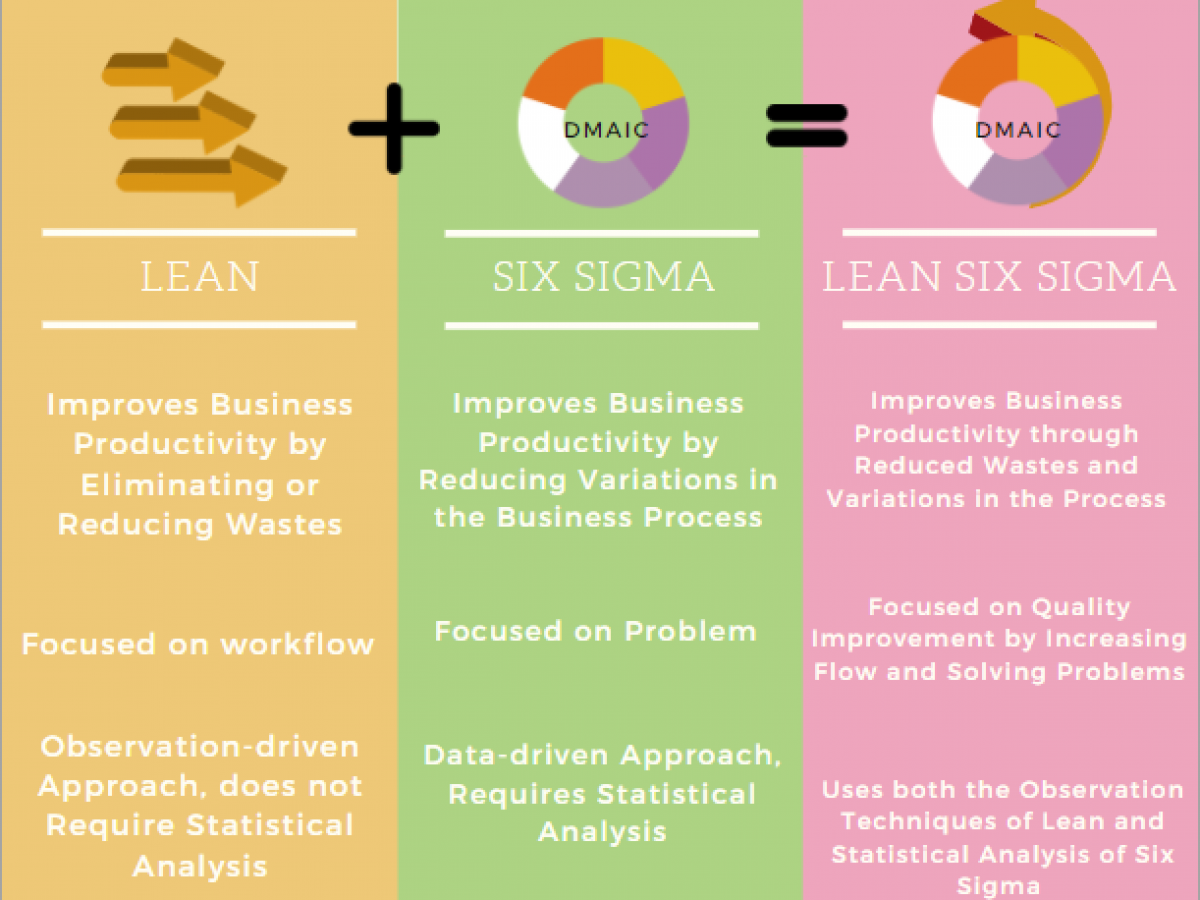
Lean Six Sigma is an integrated quality management approach combining two renowned management philosophies: Lean and Six Sigma. This model focuses on waste reduction, process optimization, and improving the quality of products or services. Lean Six Sigma is widely used across various industries to enhance efficiency and increase customer satisfaction.
Lean
Lean is a management methodology originating from the Toyota Production System. The main goal of Lean is to eliminate waste and create maximum value for customers. Key elements of Lean include:
- Waste Reduction: Focus on eliminating non-value-adding activities (wastes such as inventory, waiting time, transportation, unnecessary processes, overproduction, product defects, etc.).
- Process Optimization: Improve steps in the process to ensure a continuous and efficient workflow.
- Creating Customer Value: Ensure that every activity in the process adds value for the customer.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a quality management methodology developed by Motorola in the 1980s. Six Sigma uses statistical tools and data analysis to minimize process variability and eliminate defects. Key elements of Six Sigma include:
- Measurement and Analysis: Use statistical tools to measure and analyze process performance.
- Continuous Improvement: Seek and implement continuous improvement measures to achieve a low defect rate (typically 3.4 defects per million opportunities).
- Customer Orientation: Ensure that process improvements meet customer requirements and expectations.
Combining Lean and Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma integrates the tools and principles of both methodologies to create a more robust quality management system. Key elements of Lean Six Sigma include:
- Data and Statistics: Use data to identify problems and measure the effectiveness of improvements.
- Waste Elimination: Focus on eliminating waste and optimizing processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Seek and implement continuous improvement measures to enhance quality and efficiency.
- Customer Orientation: Ensure that process improvements provide maximum value to the customer.
DMAIC Process
Lean Six Sigma often uses the DMAIC process for process improvement:
- Define: Identify the problem to be solved, the project scope, and improvement goals.
- Measure: Collect current data to better understand the process and the issues at hand.
- Analyze: Analyze the data to identify the root causes of the problems.
- Improve: Develop and implement solutions to eliminate the root causes and improve the process.
- Control: Establish control measures to maintain the improvements and ensure that issues do not recur.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
- Improved Product/Service Quality: Minimize defects and variability in the process, enhancing the quality of products or services.
- Increased Efficiency and Reduced Costs: Eliminate waste and optimize processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced production costs.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Meet and exceed customer expectations, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Development of a Continuous Improvement Culture: Create a work environment where everyone is focused on continuous improvement and enhancing performance.
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful quality management approach that helps organizations enhance efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction by eliminating waste and improving data-driven processes.






Leave a comment